What Is Accounting? The Basics Of Accounting
If for a CORPORATION there are seven statutory options for reorganization that would cause the corporation and shareholders to not recognize any GAIN or LOSS on the exchange of stock. Business or other transaction between persons who do not have an arm’s-length relationship (e.g., a relationship with independent, competing interests). For tax purposes, these types of transactions are generally subject to a greater level of scrutiny. A put is an option to sell a certain number of shares of stock at a stated price within a certain period.
Person in a brokerage house, bank trust dept., or mutual fund group who studies a number of companies and makes buy or sell recommendations on the securities of particular companies and industry groups. Amounts paid for stock in excess of its PAR VALUE or STATED VALUE. Also, other amounts paid by stockholders and charged to EQUITY ACCOUNTS other than CAPITAL STOCK.
(2) In insurance, the cost of specified coverage for a designated period of time. A trial BALANCE prepared at the end of an accounting period after all adjusting and closing entries have been posted; a final check on the balance of the LEDGER. Process for arriving at a comprehensive plan to solve an individual’s personal, business, and financial problems and concerns. Process by which an accounting firm’s practice is evaluated for compliance with professional standards. The objective is achieved through the performance of an independent review by one’s peers. In capital budgeting; the length of time needed to recoup the cost of capital investment.
Another part of accounting focuses on providing a company’s management with the information needed to keep the business financially healthy. Although some of the information comes from recorded transactions, many of the analyses and reports include estimated and projected amounts based on various assumptions. Generally, this information is not distributed to people outside of the company’s management. A few examples of this information are budgets, standards for controlling operations, and estimating selling prices when quoting prices for new work. One part of accounting focuses on presenting the financial information in the form of general-purpose financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, etc.) that are distributed to people outside of the company. These external reports must be prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles often referred to as GAAP or US GAAP.
Change in (1) an accounting principle; (2) an accounting estimate; or (3) the reporting entity that necessitates DISCLOSURE and explanation in published financial reports. Recording and reporting of financial transactions, including the origination of the transaction, its recognition, processing, and summarization in the FINANCIAL STATEMENTS. Certified public accountants and management accountants are two of the profession’s most common specializations. Auditors and forensic accountants are another important branch of the field. It is a more complete and accurate alternative to single-entry accounting, which records transactions only once.
We also explain relevant etymologies or histories of some words and include resources further exploring accounting terminology. Our accounting basics dictionary includes dozens of important terms. This guide includes accounting definitions, alternative word uses, explanations of related terms, and the importance of particular words or concepts to the accounting profession as a whole. Accounting software makes it possible to send invoices, reconcile bank transactions, pay your vendors and pay employees. The exact software you need will depend on the type of business you run and the specific features you want. Accounting is how finances are tracked by an individual or organization, such as a small business.
Journal Entry
Managerial accounting includes budgeting and forecasting and cost analysis. As well as financial analysis, reviewing past business decisions and more. This is what managers need to make decisions about a business’s operations, not comply strictly with GAAP. There are many different types of accounting degrees, with undergraduate-level titles such as Bachelor of Accountancy or Bachelors in Accounting. You’ll need to undertake professional training after your degree, if you want to become a chartered accountant.
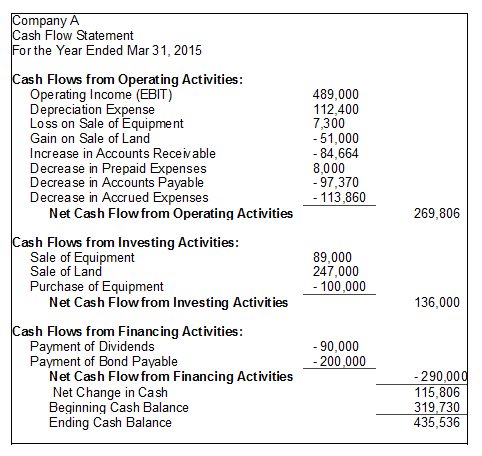
The role of an accountant is to responsibly report and interpret financial records. Written by the GENERAL ACCOUNTABILITY OFFICE, the yellow book sets forth standards to be followed in auditing the FINANCIAL STATEMENTS of entities that receive federal financial assistance. (5) Also if the exercise price of an option grant differs from the closing market price per share on the grant date companies must include a description of the method for determining the exercise price. One of the basic FINANCIAL STATEMENTS that isGENERALLY ACCEPTED ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES (GAAP) required as part of a complete set of financial statements prepared in conformity with . It categorizes net cash provided or used during a period as operating, investing and financing activities, and reconciles beginning and ending cash and cash equivalents. As distinguished from a BEQUEST or devise, an inheritance is property acquired through laws of descent and distribution from a person who dies without leaving a will.
Instead, taxable income of the corporation is passed through to its stockholders in a manner similar to that of a PARTNERSHIP. In order to be considered a RIC a CORPORATION must make an irrevocable election tax election in order to be treated as one. A ratio for measuring the relative size of a company’s accounts receivable and the success of its CREDIT and collection policies during an accounting period. Investor-owned TRUST which invests in real estate and, instead of paying income tax on its income, reports to each of its owners his or her pro rata share of its income for inclusion on their income tax returns. This unique trust arrangement is specifically provided for in the INTERNAL REVENUE CODE.
Financial Accounting participants may be eligible for financial aid based on demonstrated financial need. To receive financial aid, you will be asked to provide supporting documentation. There are nearly 40 apprenticeships in the legal, finance and accounting sector available in England, with more in development. You’ll spend around 12 hours each week in the classroom as an accounting student, but you’ll have a lot of self-study and solo projects to be tackling in your spare time.
Management Accounting
Bid is the highest price a prospective buyer is prepared to pay at a particular time for a trading unit of a given SECURITY; asked is the lowest price acceptable to a prospective seller of the same security. An economic resource that is expected to be of benefit in the future. Probable future economic benefits obtained as a result of past transactions or events. Any owned tangible or intangible object having economic value useful to the owner.
A periodic statement, usually monthly, that a bank sends to the holder of a checking account showing the balance in the account at the beginning of the month, during, and at the end of the month. A way of arriving at the cost of inventory that computes the average cost of all goods available for sale during a fixed period in order to determine the value of inventory. Auditing standards encompass the auditor’s professional qualities, as well as his or her judgment in performing an AUDIT and in preparing the AUDITORS’ REPORT. Application of an AUDIT procedure to less than 100% of the items within an account BALANCE or class of transactions for the purpose of evaluating some characteristic of the balance or class. The written record of the basis for the AUDITOR’s conclusions that provides the support for the auditor’s representations, whether those representations are contained in the auditor’s report or otherwise.
Free Cash Flow
When two or more persons or organizations gather CAPITAL to provide a product or service. A customer order for a specific number of specially designed, made-to-order products. The practice of putting money into something, such as property, in order to earn INTEREST or make a profit. Tangible property held for sale, or materials used in a production process to make a product. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS that report the operations of an entity for less than one year.
- One well-known alternative is International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).In the United States, privately held companies are not required to follow GAAP, but many do.
- Check out our review of QuickBooks accounting software and our Zoho Books review for examples of top software providers.
- The financial STATEMENT that shows how and why an OWNER’S EQUITY, or capital, ACCOUNT has changed over s specific financial PERIOD.
- Accounting is one of the backbones of the modern world, and the backbone of business.
- SECURITIES borrowed from a broker’s INVENTORY, other MARGIN accounts, or from other brokers, when a customer makes a short sale and the securities must be delivered to the buying customer’s broker.
Obligation whose LIQUIDATION is expected to require the use of existing resources classified as CURRENT ASSETS, or the creation of other current liabilities. A tax exempt trust exclusively for the purpose of paying qualified higher education costs of the trusts designated beneficiary. Rate of return that a business could earn if it chose another investment with equivalent risk.
Market Price
Financial instruments whose characteristics and value depend on the characterization of an underlying instrument or asset. Qualified child care expenses will allow a taxpayer this computed credit against tax. The amounts can be found on the individual forms as the limitations and computation may change each tax year. The TAX that an incorporated business must pay to the federal government and, often, to state and city governments as well.
Payroll Accounting
Small businesses and individuals tend to use cash basis Accounting. An accounting period defines the length of time covered by a financial statement or operation. Examples of commonly used accounting periods include fiscal years, calendar years, and three-month calendar quarters. An accounting cycle is an eight-step system accountants use to track transactions during a particular period. Accounting is a term that describes the process of consolidating financial information to make it clear and understandable for all stakeholders and shareholders.
Teaching is usually classroom-based, involving individual and group exercises, case studies, lectures, seminars and IT workshops, including the use of accounting software. Accounting revolves around the reporting and analysis of how money flows in and out of a business, ensuring that regulations are complied with and challenges are avoided. Whereas you might only periodically consult your accountant, a bookkeeper touches base more frequently and handles daily accounting tasks. Regardless of who you hire, knowing basic accounting principles can help you understand your business better and have more productive conversations with your financial team. Let’s say a client just paid their invoice online, or money was withdrawn from your checking account to pay a utility bill. Most business owners opt for small-business accounting software to help automate the process and reduce the likelihood of error.



